Chinese medicine scholars develop tumor-specific aptamer-drug conjugate
December 01, 2017
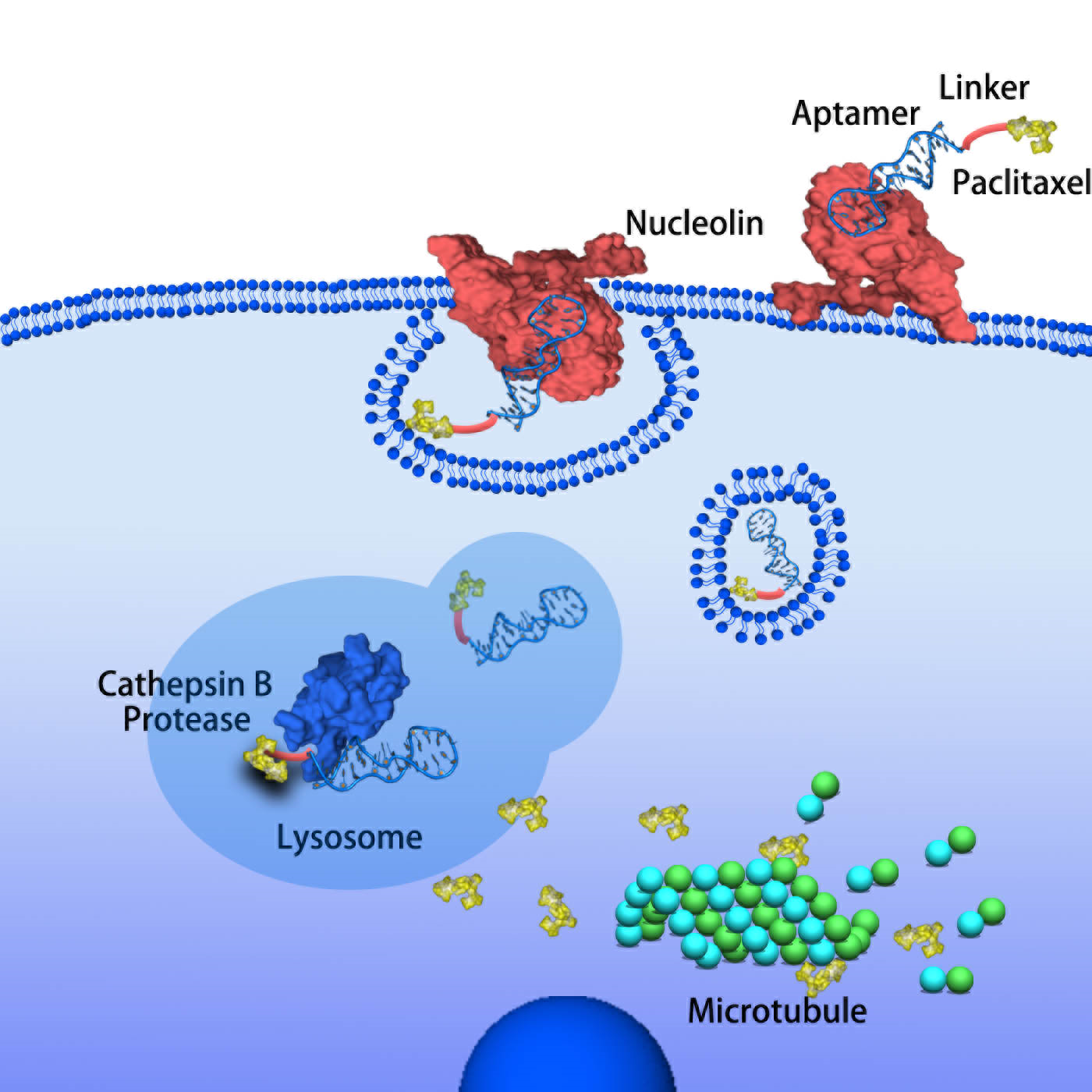
Toxicity of cancer chemotherapy is a great clinical challenge, mainly due to the chemo drugs could not distinguish cancer cells from normal cells. Chinese medicine scholars devote their efforts to the development of next generation smart anti-cancer drug molecules: tumor-specific aptamer-drug conjugate. Their research paper entitled “A water-soluble nucleolin aptamer-paclitaxel conjugate for tumor-specific targeting in ovarian cancer” was recently published in the internationally renowned academic journal Nature Communications (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-017-01565-6). The research team is led by Professor Lyu Aiping, Dean of the School of Chinese Medicine (SCM), and Professor Zhang Ge, Director of Technology Development Division and Associate Director of Teaching and Research Division of SCM.
Aptamers are single strand oligonucleotides that could form 3D structures and bind to specific cell types or proteins. They have been widely used for targeted drug delivery of small molecules and siRNAs due to their advantages such as good water solubility, low immunogenicity, high permeability and stability. To date, nucleolin aptamer has been proved with safety and tumor specificity. By conjugating nucleolin aptamer with a first line chemo drug paclitaxel into one molecule, the aptamer could improve both water solubility and tumor-targeting of the conjugated paclitaxel. The research team used an enzyme sensitive linker, and it helps the conjugate remain stable in the circulation, and release paclitaxel in tumor cells. The results showed that the conjugate exhibited excellent antitumor activity and decreased toxicity.
Other researchers who participated in the research include SCM’s Research Assistant Professor Dr Li Fangfei, Post-doctoral Research Fellow Dr Lu Jun, Post-doctoral Research Fellow Dr Liu Jin, Post-doctoral Research Fellow Dr Liang Chao, and the research team of Dr Zhang Baoting of the School of Chinese Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong.
Research paper-related video:
http://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XMTc4MjcyMzA1Ng==.html?tpa=dW5pb25faWQ9MTAyMjEzXzEwMDAwMl8wMV8wMQ。
Copyright © 2018 Institute for Precision Medicine & Innovative Drug. Privacy Policy



